A few simple, easy to understand presentations on Ratio analysis. Useful for Business A level and the Mini MBA:
Monday, 27 November 2017
Tuesday, 21 November 2017
Theorists - This list will grow!
I will put together a list of the theorists you need to understand. Mostly, you will see these in multiple choice questions, but you could/should refer to them in case studies where relevant.
Carroll's Corporate Social responsibility Pyramid - click here
Greiner's Growth Model - Click here
Bowman's Clock Strategy - Click here
Carroll's Corporate Social responsibility Pyramid - click here
Greiner's Growth Model - Click here
Bowman's Clock Strategy - Click here
Friday, 17 November 2017
Wednesday, 15 November 2017
Business Theorists - 4 examples
Below are links which will take you to a few of the business theorists that you need to know and understand how it affects business strategy. Essential reading, not just for the mock, but to develop your understanding of how business' formulate strategy.
Click here for Caroll's CSR Pyramid
Click here for Ansoff's Matrix
Click here for Bartlett & Ghoshal - international strategies
Click here for Handy's organisational culture
Click here for Caroll's CSR Pyramid
Click here for Ansoff's Matrix
Click here for Bartlett & Ghoshal - international strategies
Click here for Handy's organisational culture
Labels:
ansoff matrix,
Bartlett & Ghoshal,
business theorists,
Caroll's CSR Pyramid,
Handy's organisational culture
Monday, 13 November 2017
Porters 5 Forces - Adidas, Toyota Ikea
Adidas from subhash kalal
Sunday, 12 November 2017
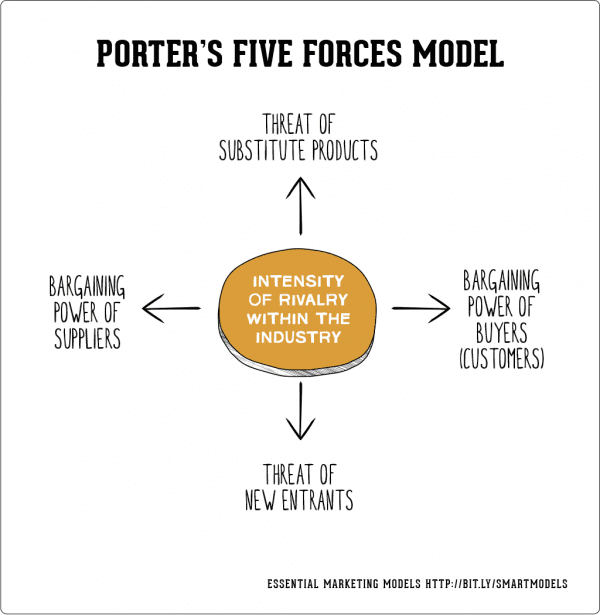
Porters 5 Forces - Worked example
What is Porter’s five Forces model?
This model helps marketers and business managers to look at the ‘balance of power’ in a market between different types of organisations, and to analyse the attractiveness and potential profitability of an industry sector.
It’s a strategic tool designed to give a global overview, rather than a detailed business analysis technique. It helps review the strengths of a market position, based on five key forces.
Porter’s Five Forces works best when looking at an entire market sector, rather than your own business and a few competitors.
How can I use Porters five Forces?
To apply Porter’s Five Forces, you need to work through these questions for each area:
- Force 1: Threat of New Entry?
- Force 2: Buyer Power?
- Force 3: Threat of Substitution?
- Force 4: Supplier Power?
- Force 5: Competitive Rivalry?
Threat of New Entry
If a new businesses can be easily started up in your sector without substantial investment - then this is a threat. The Internet has made this a reality in many sectors, especially publishing! So ask yourself the questions:
- What’s the threat of new businesses starting in this sector?
- How easy is it to start up in this business?
- What are the rules and regulations?
- What finance would be needed to start-up?
- Are there barriers to entry which give you greater power?
Buyer Power
Where there are fewer buyers, they often control the market. Questions here include:
- How powerful are the buyers?
- How many are there?
- Can the buyers get costs down?
- Do they have the power to dictate terms?
Threat of Substitution
If there are available alternatives then the threat of substitution increases.
- How easy is it to find an alternative to this product or service?
- Can it be outsourced? Or automated?
Supplier Power
Markets where there are few suppliers means the suppliers retain the power
- Examine how many suppliers are in the market?
- Are there a few who control prices?
- Or many so prices are lower?
- Do your suppliers hold the power?
- How easy is it to switch, what’s the cost?
Competitive Rivalry
Markets where there are few competitors are attractive but can be short-lived. These are highly competitive markets with many companies chasing the same work reduce your power in the market.
- What’s the level of competition in this sector?
- What’s the competitor situation? Many competitors and you’re all in a commodity situation or a few?
Examples of how Porter's five Forces can be applied to a business?
If your business is thinking about moving into new sectors or markets, or if your business is stuck in a commodity situation, then Porter’s Five Forces enables you to see the issues clearly.
Work through each of the forces to identify in your current sector and your potential sectors, to see who has the power.
Here are some examples of where the balance of power lies in different markets
- 1. Threat of New Entrants
An example is web design, as there are independents in every location. This is an easy market to enter with few requirements, other than skills, initiative and relevant hardware and software. This does mean there are many new entrants!
- 2 . Buyer Power
An example is the grocery sector since supermarkets tend to retain power over suppliers due to volume and price of contracts. They dictate terms, set prices and can possibly end agreements at any time.
- 3. Threat of Substitution
The substitute to all services is DIY. For example hairdressing or writing a will. Focus is on expertise, customer service or added value.
- 4. Supplier power
Some sectors have monopolistic (one) or oligopolistic (few) suppliers, such as utility companies. Sometimes customers have little choice i.e. where to buy domestic water suppliers though this is changing.
In the jewellery sector, diamond suppliers often hold the power and can set prices, withhold supply and restrict sales.
- 5. Competitive rivalry
These include Estate agents, web design and office stationary. Many competitors often buy on price.
What to watch for?
Sometimes not all the information is available and you may need to make assumptions, which should be shared. For example it’s difficult getting specific market information on parts of the Middle East and China.
Monday, 6 November 2017
CSR - More case studies on effectiveness
Your aim today, is to look at a firm of your choice and discuss the CSR that they do, linking it the factors listed in the chart opposite.
Sunday, 5 November 2017
Monday, 30 October 2017
External Influences: Business & Technology
A revision presentation focusing on the “T” in PESTLE - technology. The role of technological change as an opportunity or threat is examined, as are the drivers of innovation and the process of diffusion.
Labels:
external factors,
PESTLE,
SWOT analysis,
technology
Saturday, 21 October 2017
Distribution Channels made simple
Click here to access a presentation on channels of distribution!
Leadership Vs Management
Wednesday, 18 October 2017
External Factors - Latest UK Inflation Figures are released
Click here to access an article from the BBC on the latest rate of inflation data!
What does this mean for interest rates?
What does this mean for pay and living standards in the UK?
Why has this happened?
What does this mean for interest rates?
What does this mean for pay and living standards in the UK?
Why has this happened?
Sunday, 15 October 2017
External Factors - Interest rates, Inflation, Unemployment, Exchange Rates & GDP
This post will form the next 2 weeks lessons in Buisness. Click on the following link to start the show!
Interest rates - An Interactive Guide
Labels:
exchange rates,
external factors,
gdp,
inflation,
interest rates,
unemployment
External Factors - Business Legislation
A revision presentation that guides you through the relationship between business and legislation (the “L” in PESTLE analysis). It outlines the main purposes of legislation in the business environment - including consumer protection, environmental laws, competition policy and health & safety.
It also provides some recent case studies of firms and industries affected by changes in legislation.
Wednesday, 4 October 2017
International Competitiveness - Where best to set up a business
The Global Competitiveness Report has just been released, and the World economic Forum's Margareta Drzeniek-Hanouz discusses some of its more surprising findings. Watch to see which countries slipped in the ranks. Where is the UAE? Where is Pakistan, India, the UK?
Click on this link to find out! Really useful when looking at how a country can help individual businesses make decisions on where to invest.
Click on this link to find out! Really useful when looking at how a country can help individual businesses make decisions on where to invest.
Saturday, 30 September 2017
Big companies = big debt (Gearing Ratio)
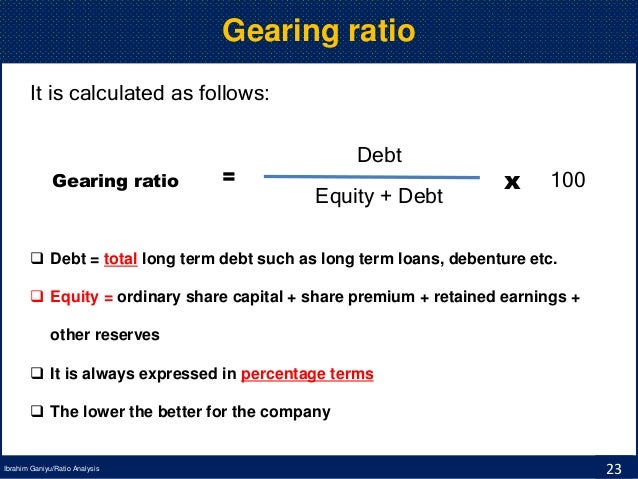 Click here to access an interesting article on why big companies actually like to highly geared Obviously this is a little tongue in cheek, but it is useful when discussing the issues of being in debt and the possible advantages/ reasons behind this.
Click here to access an interesting article on why big companies actually like to highly geared Obviously this is a little tongue in cheek, but it is useful when discussing the issues of being in debt and the possible advantages/ reasons behind this.The diagram opposite has a flaw in its explanation of gearing. What is it?
Tuesday, 26 September 2017
SWOT Analysis - Revision Presentation
SWOT Analysis from tutor2u
Saturday, 16 September 2017
Corporate Strategy and Specimen Question
Introduction to Corporate and Functional Objectives from tutor2u
Click here to access another presentation on business strategy.
Use the above resources to answer the following question:
Under Justin King, Sainsbury’s changed its strategy. Do you think that to be successful the strategy of a business needs to be determined mainly by what is happening in its external environment? Justify your answer. [24 marks]
Click here to access another presentation on business strategy.
Use the above resources to answer the following question:
Labels:
business objectives,
corporate strategy,
objectives,
strategy
Wednesday, 13 September 2017
Mission Statement - Essay
Using examples to illustrate your answer, explore the idea that mission statements should reflect an organisation’s purpose.
Tuesday, 12 September 2017
Mission Statements - presentation and examples
Definition: A formal statement which explains the overriding purpose and values of a business.
BSAK Vision: Building on our unique local heritage, we will provide a world-class British education, inspiring all our students to exceed expectations.
BSAK Mission Statement: Providing the best teachers, leadership and support in a not-for-profit environment, we nurture a genuine passion for learning.
Presentation on importance and relevance of mission statements.
What makes a good mission statement?
Click here to access 50 examples of mission statements for not for profit companies.
BSAK Vision: Building on our unique local heritage, we will provide a world-class British education, inspiring all our students to exceed expectations.
BSAK Mission Statement: Providing the best teachers, leadership and support in a not-for-profit environment, we nurture a genuine passion for learning.
Presentation on importance and relevance of mission statements.
What makes a good mission statement?
- The best mission statements are clear, concise, and useful (informs. focuses. guides.)
- Avg length for the full 50 organizations listed here is only 15.3 words (excluding brand references)
- Avg length for the first 20 organizations below is only 9.5 words (excluding brand references).
- The shortest contains only two words (TED)
- The longest contained 235 words (UNHCR)
Click here to access 50 examples of mission statements for not for profit companies.
Monday, 12 June 2017
AQA Paper 1: 25 Mark Essays
The first sitting of Paper 1 is just around the corner. In addition to the practice 25 mark questions we provided in the AQA Grade Booster revision workshops for 2017 here are 8 more essay questions to have a think about.
Rather than write out full answers for these essays, spend 5-10 minutes thinking about how you would respond to them:
- What is the evaluation hook?
- What is the context you need to use?
- What are you main arguments and how could you use models / theories & lines of analysis to develop them?
- What evaluation could you add for your slice of PiE in each paragraph point?
- What is your judgement and why?
SECTION C
In recent years we have seen the emergence of low-cost competitors undercutting market leaders in many industries. As a result, to what extent is price now the most important part of the marketing mix for market leaders trying to remain competitive?
It is increasingly argued that the boards of public companies are too concerned with short-term performance rather than acting in the long-term interests of shareholders. To what extent do you agree that a more long-term perspective in decision-making by public companies would be more likely to improve the profits and share price of such companies?
High-profile multinationals such as Toyota and Samsung have suffered significant losses in recent years after widespread problems with quality. To what extent do you agree that achieving a high level of quality should be the most important operational objective for businesses that want to compete globally?
The managers of a large supermarket group want to achieve a significant improvement in the standard of customer service. To what extent will financial methods of motivation be more likely than non-financial methods of motivation to help achieve this objective?
SECTION D
The rapid pace of technological change has disrupted business models in many markets and industries. As a result, to what extent do you agree that only organisations that innovate will succeed in the long-term?
To what extent do you agree that a large business that needs to undergo a significant change programme must first change the leadership of the business?
Do you agree that external growth is the best way for multinational businesses to take advantage of opportunities in fast-growing international markets?
In recent years businesses have shown increasing interest in the impact of their activities on the environment. Do you agree that operating in a sustainable way is now the most important responsibility of a business?
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)